- Methane is synthesized commercially by distilling bituminous coal and by heating a mixture of carbon and hydrogen. It can be produced in the laboratory by heating sodium acetate with sodium hydroxide and by the reaction of aluminum carbide (Al4C3) with water.
- Methane is the product of the anaerobic bacterial decomposition of vegetable matter under water (hence its alternate name, marsh gas).
- This compound is produced in environments with little or no oxygen by bacteria that feast on decomposing organic matter, such as waste deposits like landfills. Since piles of garbage are stacked and little oxygen is present it allows the bacteria to eat away on decomposing organic matter producing methane gas.
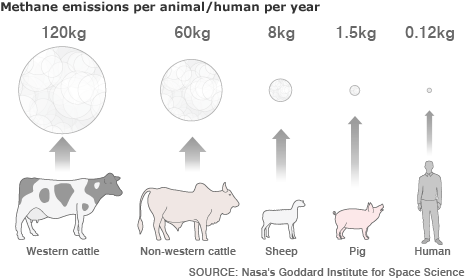
- Methane is also produced in the stomachs of cattle since some plants and many animals emit methane as a by-product of food digestion.
- Methane is released while obtaining it from underground reservoirs for industrial use, while pumping oil, and while mining coal.
- A substantial amount of methane also originates from the burning of forests and other vegetation. Almost half of the world's methane comes from natural sources such as wetlands, rivers and streams, gas hydrates on the ocean floor, and permafrost. (Methane, 2008). (Palmer, n.d.).
- Methane is the product of the anaerobic bacterial decomposition of vegetable matter under water (hence its alternate name, marsh gas).
- This compound is produced in environments with little or no oxygen by bacteria that feast on decomposing organic matter, such as waste deposits like landfills. Since piles of garbage are stacked and little oxygen is present it allows the bacteria to eat away on decomposing organic matter producing methane gas.
- Methane is also produced in the stomachs of cattle since some plants and many animals emit methane as a by-product of food digestion.
- Methane is released while obtaining it from underground reservoirs for industrial use, while pumping oil, and while mining coal.
- A substantial amount of methane also originates from the burning of forests and other vegetation. Almost half of the world's methane comes from natural sources such as wetlands, rivers and streams, gas hydrates on the ocean floor, and permafrost. (Methane, 2008). (Palmer, n.d.).