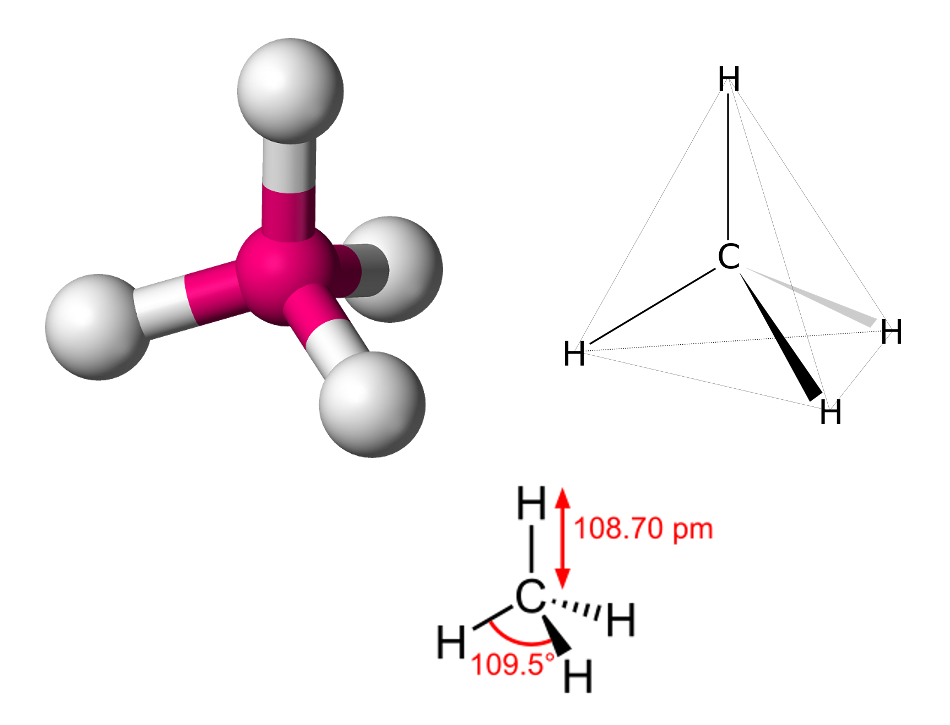
- The electronegativity for methane is 0.4 which means that it has a non-polar covalent
bond.
- Since methane is nonpolar the intermolecular forces between them are Van der Waals forces.
- The electrons in methane are always moving. At any instant, they might be at one end of the molecule which instantaneously creates a temporary dipole, making that end negative and the other end positive. The positive charge attracts the electrons in an adjacent methane molecule. This temporary attractive force is the Van der Waals force which is so weak that methane does not condense to a liquid until it cools to −161.50 °C. (Ernest, 2014).
- Since methane is nonpolar the intermolecular forces between them are Van der Waals forces.
- The electrons in methane are always moving. At any instant, they might be at one end of the molecule which instantaneously creates a temporary dipole, making that end negative and the other end positive. The positive charge attracts the electrons in an adjacent methane molecule. This temporary attractive force is the Van der Waals force which is so weak that methane does not condense to a liquid until it cools to −161.50 °C. (Ernest, 2014).